
A pre-flight check should be executed...
Before you take off, you should check at least these things: pilot, lines, canopy, wind, airspace.
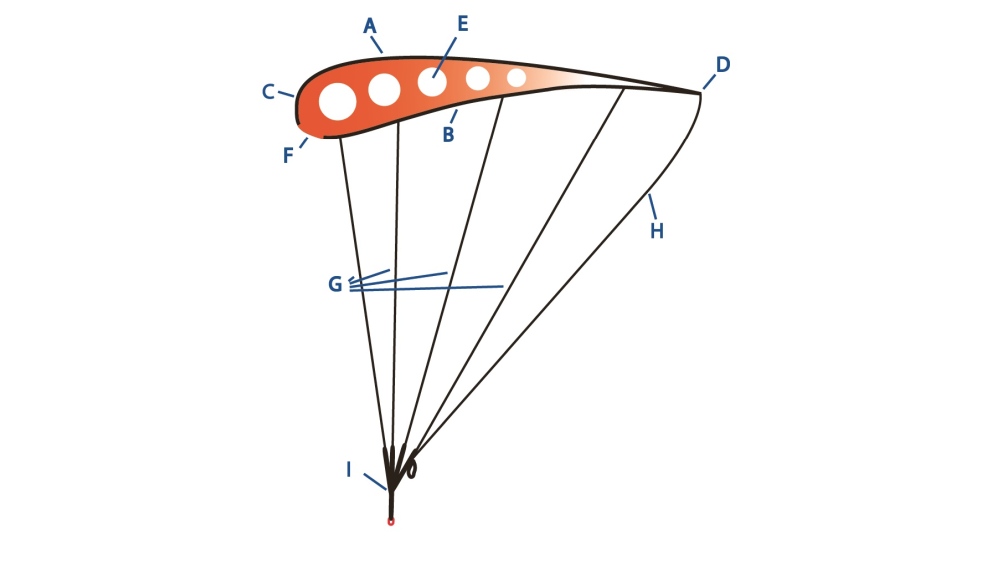
Which lines carry the most weight?
Most of the weight is carried by the lines attached to the front of the canopy.

What is the weight of the fabric used to make paraglider canopies? (g/m2)?
Very light fabric strong enough for paragliders can be as light as 25g/m2. Very strong and heavy fabric weighs 40g/m2 or more.
At around 35g/m2, you can calculate that the weight of the fabric of just the top and bottom sail of a 25m2 canopy is a bit less than two kilos.

Despite a good flare, you have a lot of speed just before touching down, because you landed with the wind in your back. What do you do?
A is the safest option if you're not familiar with a PLF (parachute landing fall) which needs practise. Your legs are much stronger than your back or arms.
Although on a flat grassy surface, you could get away with answer B, it can be very dangerous when stones, holes or other objects are hidden in the grass.
Using the protection in your harness as a landing option is not safe - would you park your car against a wall at full speed because the airbags will catch the blow?
You just landed. What do you do?
Directly after landing, look around for other gliders that are about to land and clear the landing area as quickly as possible, without disturbing others.
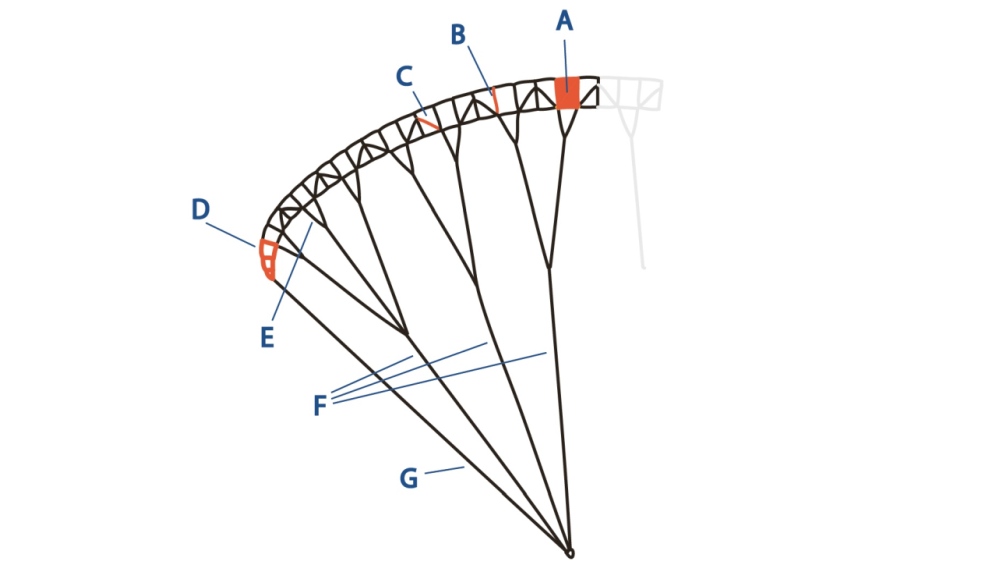
What part is indicated by C (the orange line)?
A diagonal rib connects the upper left corner of a cell with the lower right, or sometimes runs across two or more cells.
This allows the use of fewer lines, reducing the weight and drag of the paraglider.
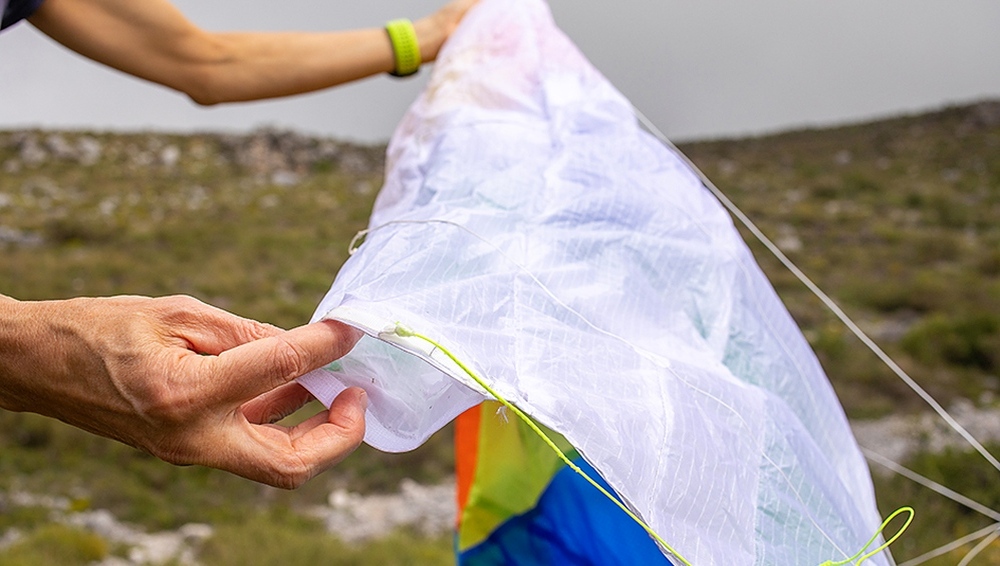

During daily inspections you notice a tear of about 2.5cm or one inch in the canopy of your paraglider. What do you do?
1. You fix the tear with ripstop tape on both sides of the fabric.
2. You take the glider to a dealer or manufacturer to have it professionally repaired.
You can fix a tear smaller than about 5cm (2 inches) yourself. Larger repairs should be done by a professional.
See the chapter on Equipment.
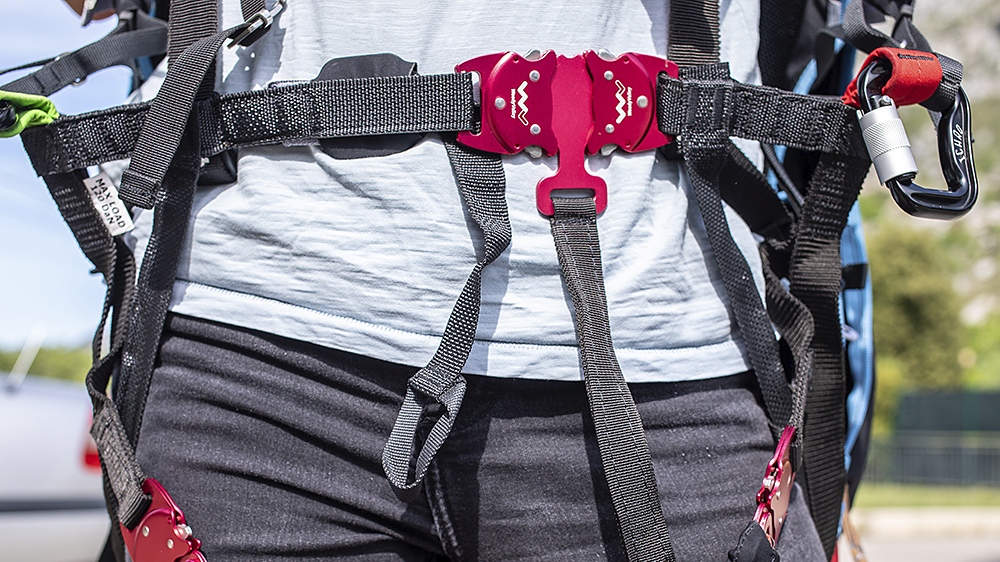

How tight does the chest strap of the harness need to be?
A short distance beween the karabiners results in a stable flight but enhances the risk of twisting, for example after a collapse.
A large distance between the karabiners results in a higher sensitivity to weight shift but also to more dynamic reactions of the paraglider.
A paraglider glides down through the air. But at what speed?
These are all speeds relative to the air!
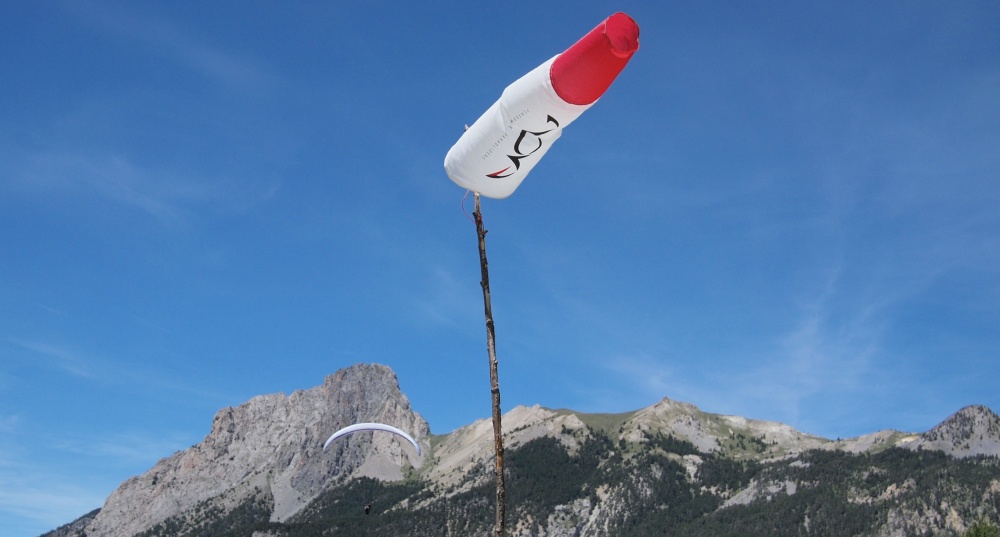

For a paraglider in the mountains, what wind speeds are considered safe to fly?
Wind results in turbulence in the mountains. While soaring on a ridge or at low dunes or flying in flatlands may be safe up to 4 Bft or a bit higher using a smaller mini-wing, in the mountains a wind speed up to 3 Bft (a maximum of 20 km/h) is the maximum for most pilots to fly safely. Strong winds are considered 25 km/h or over.
Your result is shown above.
Did you like our quiz?
Share your result with your friends using the buttons below.