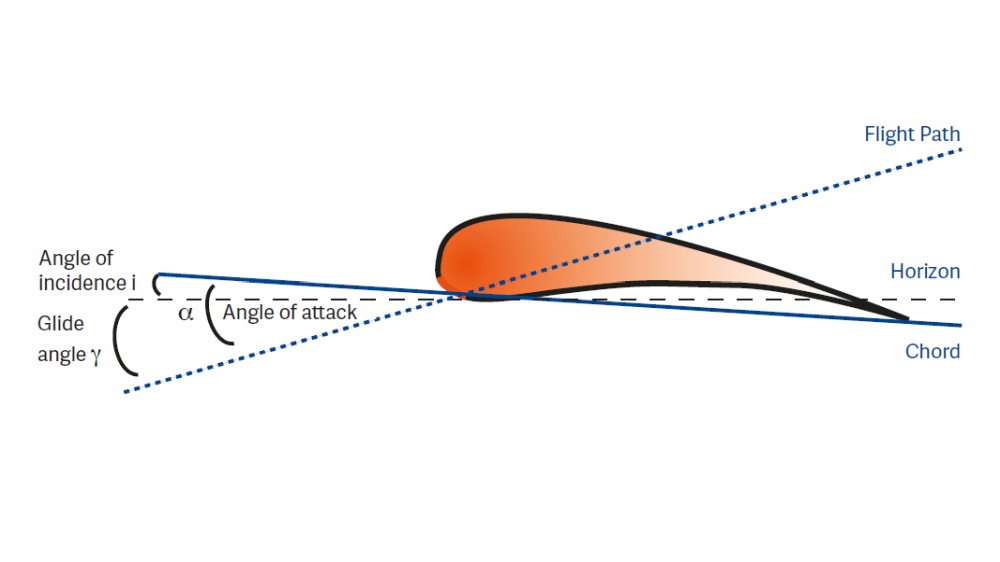
A paraglider is flying at low airspeed. What is the effect of increasing the angle of attack?
At low airspeed, the angle of attack is already high. Increasing it even more (by braking for example) will decrease lift and increase drag even more, bringing the airfoil closer to its stall point.
See the sections on Lift and drag in the Aerodynamics chapter.
.jpg)
You are flying on tow when suddenly the tow line snaps somewhere down low. Do you keep flying with the rest of the line still attached to your harness?
The best technique is to release the tow line but hold on to the line and bring it in as far as possible so it can't get stuck on an object on the ground. Dropping the line may cause it to fall over houses, roads, trees or people, but in an emergency, such as the line getting stuck and pulling you, you should immediately release and drop the line.
See the section on tow launch in the chapter on Basic techniques.
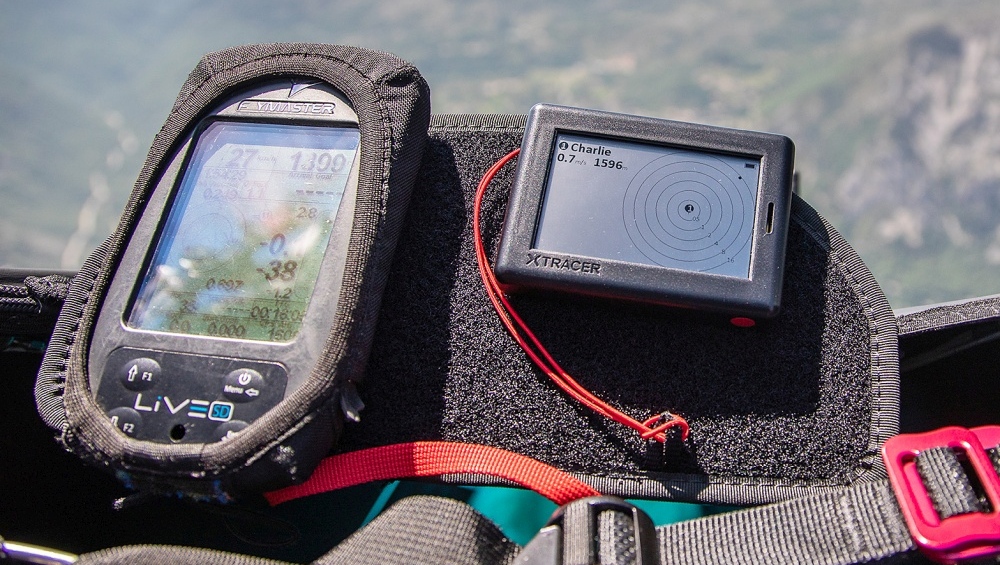

Which of these instruments is suitable to measure groundspeed?
A GPS calculates your position on (or above) the earth in time intervals. Therefore it can tell you your groundspeed as well.
A TAS measures True Air Speed. An anemometer measures wind speed. A variometer measures ascent and descent rates.

Which distance must a paraglider keep with respect to other aircraft?
How much is 'enough' depends on the situation! See the chapter on Rules and regulations.
What is the air pressure at sea level and how does the air pressure change with altitude?
Air pressure at sea level varies quite a bit over the earth. On average it is 1013,25hPa in what we call the Standard Atmosphere. Air pressure decreases with altitude, but not linearly. At 5500m it is 505hPa in the Standard Atmosphere, which is half of that at sea level.

What is the approximate minimum breaking strength of a tow line?
See the chapter on equipment. 1 kN equals a force of 100 kg. The breaking strength should of course not be equal to or below the weight of an average paraglider. Therefore 6 kN or 600 kg is the only feasible answer.
Which of the following statements about a Nautical Mile (NM) is not correct?
A NM is 1852 meter.
A statute mile is 1609 meter.
See the paragraph on Navigation.
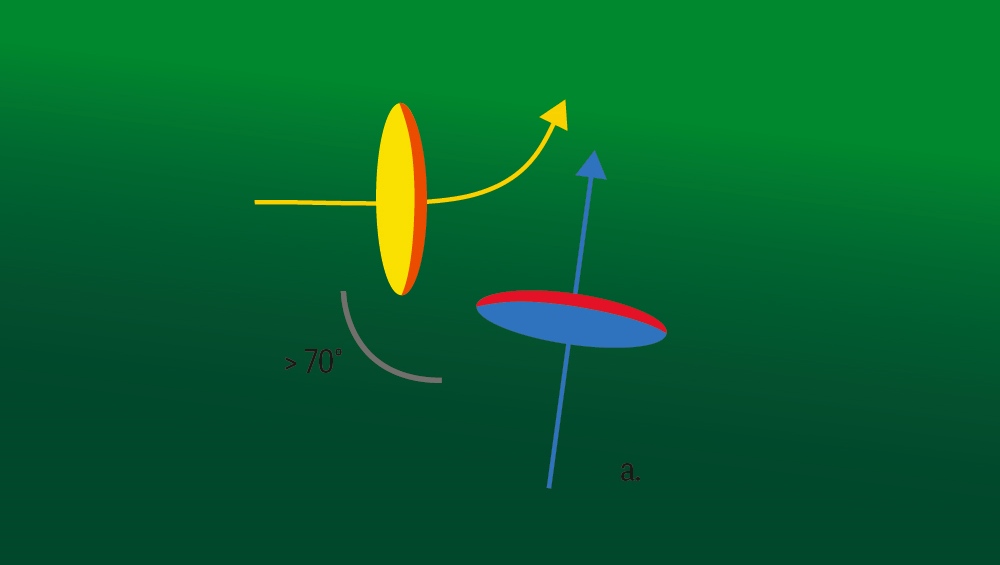
When the course of two paragliders crosses at the same altitude, what do they do?
On the right is in the right. The one coming from the left gives way.
See the chapter on Rules and regulations

Your wing collapses on the right hand side. What is the first thing you do?
Most collapses will reinflate spontaneously. Therefore it is most important to keep your course by weightshifting and applying a bit of brake if necessary and avoid obstacles or other pilots. Then look up and see if you need to solve the collapse.
See the section on Incidents in flight in the chapter on Advanced flying.
FL095 is...
FL095 means Flight Level 9500 feet. Flight level is an aircraft's altitude at standard air pressure indicated in hundreds of feet.
Your result is shown above.
Did you like our quiz?
Share your result with your friends using the buttons below.